Understanding the Differences Between Symbolic and Connectionist AI

TL;DR
- This article covers symbolic AI, which uses explicit rules and logic, versus connectionist AI, which mimics the human brain with neural networks. It includes knowledge representation, learning methods, strengths, weaknesses, and real-world applications of each approach. Also, it explores hybrid models combining both for enhanced AI solutions, offering insights for strategic tech decisions.
Introduction: The Two Paths to Artificial Intelligence
Okay, so, ai... it's kinda like having two different blueprints for building a brain, right?
- Symbolic ai is all about rules, like telling a computer exactly what to do. Think chess programs, where every move is calculated.
- Connectionist ai, on the other hand, learns from data, kinda like how we learn. Neural networks are a prime example.
It's an ongoing debate which is "better" – but honestly, does it even matter? As GeeksforGeeks explains, each has strengths and weaknesses. The general consensus is that the "better" approach often depends on the specific task. Symbolic AI is generally preferred for tasks requiring precise, explainable logic, while connectionist AI excels at pattern recognition in complex, unstructured data. Let's dive deeper, shall we?
Understanding Symbolic AI: Rules and Logic
Symbolic ai, huh? It's kinda like giving a computer a really, really detailed instruction manual.
Symbolic ai operates on explicitly programmed rules and symbols. Think of it like this: you're teaching a computer how to play chess by giving it all the rules – how each piece moves, what checkmate is, etc. It doesn't learn chess; it just knows the rules.
Knowledge is represented using symbols and logical structures. So, in our chess example, each piece would be a symbol (pawn, rook, queen), and the relationships between them would be the logical structure (e.g., "the queen can move any number of squares diagonally").
Here's a super simple example of a rule-based system:
if patient_has_fever AND patient_has_cough:
print("Possible diagnosis: influenza")
It's not rocket science, right? if this then that—but it gets way more complex, fast.
One of the biggest strengths of symbolic ai is explainability. You can easily trace back decisions to the specific rules that were triggered. No black box here.
Symbolic ai also excels in tasks requiring precise logical reasoning. Think of tax software, for example. It needs to follow strict rules and regulations, and accuracy is paramount.
And it's pretty effective for representing structured knowledge. Imagine a legal database where laws are represented as symbols and logical relationships. It's all about organizing information in a way that the computer can "understand" and process.
But it's not all sunshine and rainbows, symbolic ai struggles with new, unforeseen situations. What happens when the chess player changes the rules mid game? It gets confused because its knowledge base is incomplete.
It also has scalability issues. As the amount of knowledge and rules increases, the system can become very complex and difficult to manage. Imagine trying to code every single possible scenario in a customer service chatbot? Yikes.
And the biggest bottleneck? Knowledge acquisition. It requires manual coding of rules, which can be time-consuming and expensive. It's like writing that instruction manual, page by page.
So, that's symbolic ai in a nutshell. It's all about rules and logic, but it has its limitations. Next up, we'll dive into connectionist ai, which takes a completely different approach.
Examining Connectionist AI: Neural Networks and Learning
Connectionist ai, huh? It's kinda wild to think about mimicking the human brain, isn't it?
Connectionist ai uses artificial neural networks, which are loosely based on how our brains are wired. Think of it like this: you got a bunch of artificial "neurons" all linked together. These networks learn from data by tweaking the connections – or "weights" – between those neurons. The stronger the connection, the more influence one neuron has on another.
It's a bit like how we learn, really. When you see a cat, certain neurons in your brain fire together. The more you see cats, the stronger those connections get, and eventually, you just know it's a cat.
So, how does a neural network actually do anything? Well, imagine feeding it an image. The network crunches the numbers and spits out a prediction. If it's wrong, the network adjusts the weights and tries again. It keeps doing this until it gets pretty good at guessing right.
One of the big wins is pattern recognition. These networks are amazing at spotting patterns in huge datasets. Think identifying fraudulent transactions in finance or predicting customer behavior in retail.
They're also adaptable. Connectionist ai can learn and adjust to new data, which is super handy in ever-changing environments.
Plus, they're pretty robust. They can handle messy or incomplete data better than you'd think.
Here's the kicker: they're often "black boxes." It's hard to know why they made a certain decision. This emergent property, where the network's decision-making process isn't directly traceable to specific rules, is a key difference from symbolic AI.
They're also data-hungry. You need tons of training data to get them working well. The more the better, honestly.
And let's not forget computational resources. Training these networks can be seriously expensive and time-consuming.
So, connectionist ai is cool, right? But it's got its downsides too. Now, let's look at how these two approaches differ more directly.
Key Differences Between Symbolic AI and Connectionist AI: A Deeper Dive
Okay, so, symbolic ai versus connectionist ai—it's not like choosing between chocolate and vanilla, but more like deciding if you want a detailed, step-by-step instruction manual or to learn by doing and trusting your intuition.
Symbolic AI operates on explicit rules and symbols that are human-readable and understandable. Knowledge is represented in a structured, logical format. Think of it as a meticulously crafted legal document or a complex mathematical proof.
Connectionist AI, on the other hand, uses neural networks where knowledge is distributed across a vast network of interconnected nodes. It learns through exposure to data, adjusting connection strengths. This is more akin to how our brains form associations and learn from experience, where understanding emerges from the collective behavior of many simple units, much like how "following your gut" relies on a lifetime of accumulated, often subconscious, experiences.
Symbolic AI requires manual knowledge engineering. Experts must define all the rules and facts. This is like a teacher meticulously preparing a textbook for students.
Connectionist AI learns from data. It identifies patterns and relationships without explicit programming. This is like a student learning by observing, experimenting, and making mistakes, gradually refining their understanding.
Symbolic AI excels at tasks requiring precise logical deduction, planning, and reasoning. Examples include expert systems for diagnostics or automated theorem provers.
Connectionist AI is a powerhouse for pattern recognition, classification, and prediction in complex, noisy, or unstructured data. This is what drives image and speech recognition, and anomaly detection.
The core trade-off lies in explainability versus adaptability. Symbolic AI offers transparency but can be brittle. Connectionist AI is highly adaptable but often operates as a black box.
Applications and Use Cases: Where Each Approach Shines
Okay, so, where do these AI approaches actually make a difference? It's not just theory, right?
Symbolic AI Applications:
- Expert Systems: Digital consultants for medical diagnosis, financial planning, or technical troubleshooting, using rule-based inference.
- Rule-Based Systems: Used in fraud detection, compliance checks, and automated decision-making where strict adherence to predefined rules is critical.
- Automated Reasoning Systems: Employed in formal verification, theorem proving, and complex game-playing engines that rely on logical deduction.
- Knowledge Representation: Building ontologies and knowledge graphs for structured data management and semantic search.
Connectionist AI Applications:
- Image Recognition: Object detection, facial recognition, medical image analysis, and autonomous driving systems.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Machine translation, sentiment analysis, chatbots, and text generation.
- Predictive Analytics: Stock market forecasting, customer churn prediction, recommendation engines, and anomaly detection in large datasets.
- Speech Recognition: Converting spoken language into text for virtual assistants and dictation software.
Next, let's look at how these individual strengths can be combined.
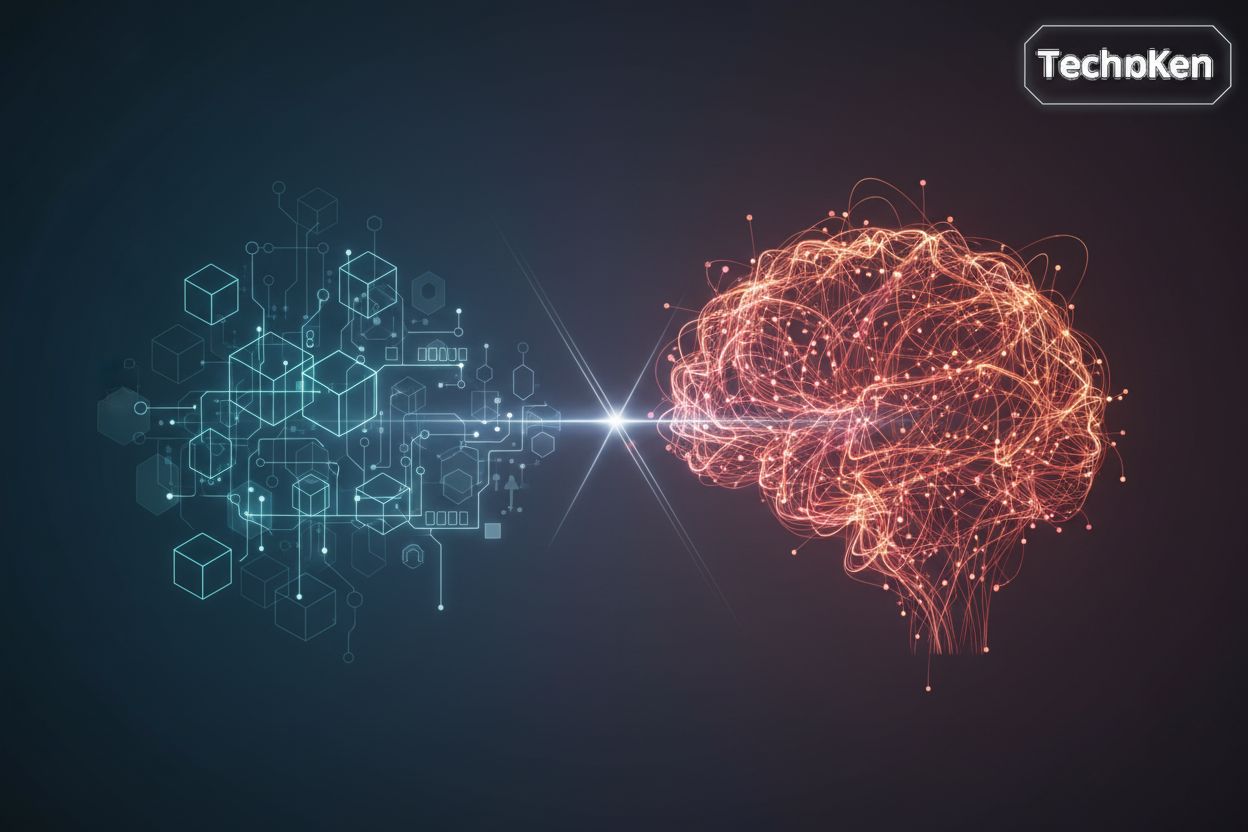
Hybrid Approaches: Combining Symbolic and Connectionist AI for Enhanced Solutions
Okay, so, ai, right? It's not just one thing, but kinda two different approaches that, honestly, work better together. Who knew? The limitations of purely symbolic or purely connectionist systems have led to the development of hybrid approaches, aiming to leverage the strengths of both.
- Enhanced Interpretability: By integrating symbolic reasoning with connectionist models, we can create systems that not only perform complex pattern recognition but can also provide explanations for their decisions. This bridges the "black box" problem of neural networks with the transparency of symbolic AI.
- Improved Learning and Robustness: Symbolic AI can provide structured prior knowledge or constraints to connectionist models, guiding their learning process and making them more efficient and robust, especially in data-scarce scenarios. Conversely, connectionist models can help extract symbolic rules from data.
- Greater Flexibility and Generalization: Combining these approaches allows AI systems to handle a wider range of tasks, adapting to new information while maintaining logical consistency and understanding.
A prominent example of this synergy is Neuro-symbolic AI. This paradigm seeks to combine the perceptual and learning capabilities of neural networks with the reasoning and knowledge representation abilities of symbolic systems.
- Visual Question Answering (VQA): Neuro-symbolic systems can process visual information (connectionist) and then use symbolic reasoning to answer questions about the image content, understanding relationships and inferring answers.
- Robotics: Robots can use neural networks for real-time perception and control, while symbolic reasoning helps them with high-level planning, task execution, and understanding their environment in a structured way.
- Natural Language Understanding: Combining deep learning for language processing with symbolic logic for semantic interpretation and reasoning.
Hybrid approaches represent a significant step forward, offering more powerful, versatile, and understandable AI solutions.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of AI
So, we've looked at the two main paths in ai: symbolic and connectionist. Symbolic ai, with its clear rules and logic, is fantastic for tasks demanding precision and explainability. It's like having a super-detailed instruction manual. On the other hand, connectionist ai, powered by neural networks, excels at finding patterns in massive datasets and learning from experience, much like our own intuition.
While each has its strengths, neither is a silver bullet. Symbolic ai can struggle with ambiguity and novel situations, while connectionist ai often lacks transparency. This is where the exciting field of hybrid approaches, particularly neuro-symbolic AI, comes into play. By merging the best of both worlds, we're building AI systems that are not only powerful but also more understandable and adaptable.
The debate about which is "better" is really evolving into a discussion about how to best combine them. The future of ai likely lies in these integrated systems, pushing the boundaries of what machines can do and how they can help us. It's a dynamic and fascinating space, and it's only going to get more interesting.